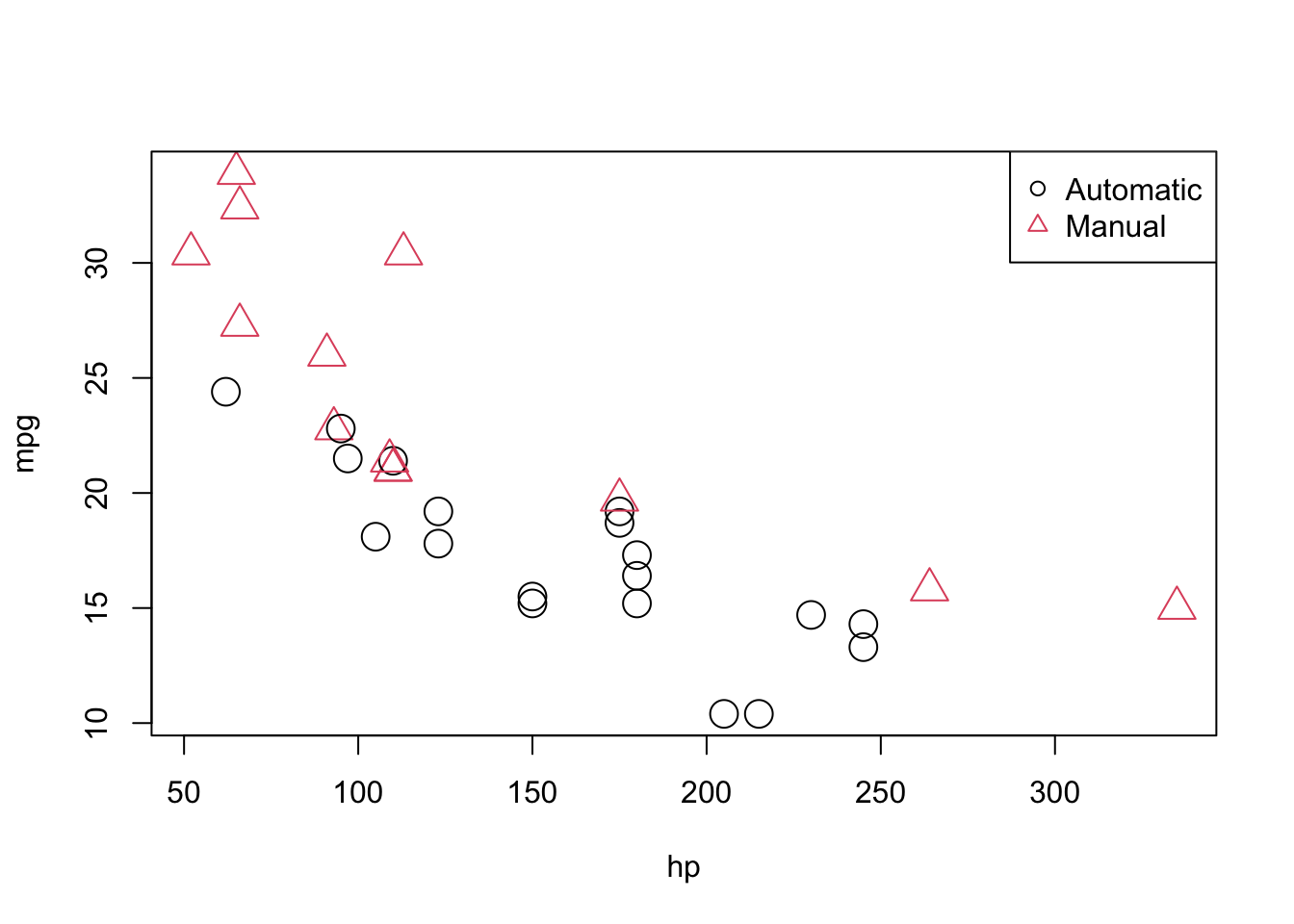
However if you add a covariate or have unequal sample sizes within each group coefficients are based on weighted means for. For example a categorical variable has the levels Fast and Slow and the reference level is Slow.
Chapter 11 Categorical Predictors And Interactions Applied Statistics With R
Interpreting the Coefficient of a Categorical Predictor Variable For a categorical predictor variable the regression coefficient represents the difference in the predicted value of the response variable between the category for which the predictor variable 0 and the category for which the predictor variable 1.
Interpreting coefficients of categorical predictor variables. Interpreting Coefficients of Categorical Predictor Variables Similarly B 2 is interpreted as the difference in the predicted value in Y for each one-unit difference in X 2 if X 1 remains constant. When models get more complicated interpretations are similar. Regression model can be fitted using the dummy variables as the predictors.
Arguably the classical effects model more clearly articulates the quantities we are interested in. You can either put Gest and Smoke_yes in the box labeled Continuous predictors or alternatively put Gest in the box. In R using lm for regression analysis if the predictor is set as a categorical.
Sampling preference you can find th. For nonlinear models such as logistic regression the raw coefficients are often not of much interest. For other values the program shows for 12 a value which is 123355 254342 377697 for 21 it predicts 6191175 which is sum of the intercept coeff and Fac12 coefficient and for 22.
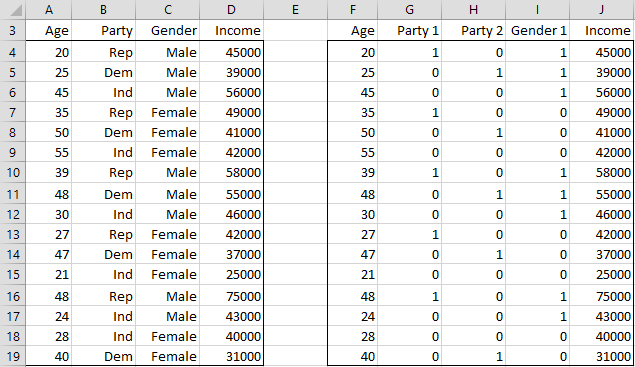
You can create the linear regression equation using these coefficients. When you perform a regression analysis with categorical predictors Minitab uses a coding scheme to make indicator variables out of the categorical predictor. In order to do so we will create what is known as an indicator variable also known as a dummy variableFor a categorical predictor Z with k levels this will require the creation of k-1 indicator variables.
Birthweight and smoking 2-level categorical predictor additive model Create an indicator variable for Smoke by selecting Calc Make Indicator Variables move Smoke to the box labeled Indicator variables for and click OK Perform a linear regression analysis of Wgt on Gest Smoke_yes. You should only interpret the coefficient of a continuous variable interacting with a categorical variable as the average main effect when you have specified your categorical variables to be a contrast centered at 0. However since X2 is a categorical variable coded as 0 or 1 a one unit difference represents switching from one category to.
Your interpretation of the models coefficients is not completely accurate. Although we primarily focus on categorical predictors with just two categories or levels the methods and concepts extend readily to general categorical variables that rather than defining just two groups define c groups. In general a categorical variable with k k levels categories will be transformed into k 1 k 1 dummy variables.
You cannot interpret it as the average main effect if. However since X 2 is a categorical variable coded as 0 or 1 a one unit difference represents switching from one. In the case of a quantitative variable you need to be aware of what you are forcing mathematic to give you something weird.
The interpretation of categorical predictors is also similar to before these coefficients are associated with the indicator variables for being in the second third or fourth quartile of the class. If the coefficient for Fast is 13 then a change in the variable from Slow to Fast increases the natural log of the odds of the event by 13. R a c e s e x and e d u c a.
Interpreting regression models Often regression results are presented in a table format which makes it hard for interpreting effects of interactions of categorical variables or effects in a non-linear models. However the predicted probabilities associated with the values of the outcome are no long simply a transformation of the coefficients. In this lesson we investigate the use of such indicator variables for coding qualitative or categorical predictors in multiple linear regression more extensively.
The interpretation of dummy variables follows the same principle. Interpreting Coefficients of Categorical Predictor Variables Similarly B 2 is interpreted as the difference in the predicted value in Y for each one-unit difference in X 2 if X 1 remains constant. The term in the parentheses is just noise a random variable with an expectation of zero which means that y 2j - y 1j is an estimate of τ 2 - τ 1The function τ 2 - τ 1 is estimable.
Let me first summarize the terms of the model. A categorical predictor variable does not have to be coded 01 to be used in a regression model. The interpretation of predictor coefficients does not change with the addition of more than one predictor when staying in the realm of interpretation involving the logit or log odds.
Which is why the caveat at the end of the previous paragraph is critically important. However since X 2 is a categorical variable coded as 0 or 1 a one unit difference represents switching from one. However since X 2 is a categorical variable coded as 0 or 1 a one unit difference represents switching from one.
I am interpreting Intercept 1233554 as a predictor for 11. Similarly B 2 is interpreted as the difference in the predicted value in Y for each one-unit difference in X 2 if X 1 remains constant. Try removing variables with high p-values from your model and observe the effect on R-squared.
Imagine you have dummy coded a variable representing gender and for the sake of this example let Male0 and Female1. The first quartile is the baseline group. We will often wish to incorporate a categorical predictor variable into our regression model.
The factor race has four levels. It is easier to understand and interpret the results from a model with dummy variables but the results from a variable coded 12 yield essentially the same results. Linking the means model with the classical effects model we have μ 2 - μ 1 τ 2 - τ 1.
Interpreting Coefficients of Categorical Predictor Variables. You can conceptualize it as the expected increasedecrease in the dependent variable for a change from 0 to 1 in the independent variable. White red green blue yellow with the correspondent value of 1 through 5.
O HR90 8962 4587RD90 1955PS90 - 049MA90 461DV90 - 524UE90 In ArcMap if the Koenker statistic is significant look at the robust p-value column. Our first example will consider a binary predictor with. Interpreting Coefficients of Categorical Predictor Variables Similarly B2 is interpreted as the difference in the predicted value in Y for each one-unit difference in X2 if X1 remains constant.
R a c e w h i t e b l a c k m e x i c a n m u l t i o t h e r. Estimated coefficients can also be used to calculate the odds ratio or the ratio between two odds. Answer 1 of 2.
Chapter 12 Regression With Categorical Variables Introduction To Statistics And Data Science

How To Use Spss One Way Anova With Post Hoc Tests Program Evaluation Anova Lean Six Sigma
Categorical Coding Regression Real Statistics Using Excel

A Gentle Introduction To Text Mining Using R Data Scientist Data Science Data Analytics

5 Types Of Regression And Their Properties Data Science Regression Science

How To Interpret Regression Function With Categorical Variable Cross Validated

Introduction To R For Data Science Session 7 Multiple Linear Regression Model In R Categor Data Science Linear Regression Machine Learning Deep Learning

All About Categorical Variable Encoding By Baijayanta Roy Towards Data Science

How To Interpret Categorical Variables With Many Categories Logistics Regression Spss Cross Validated
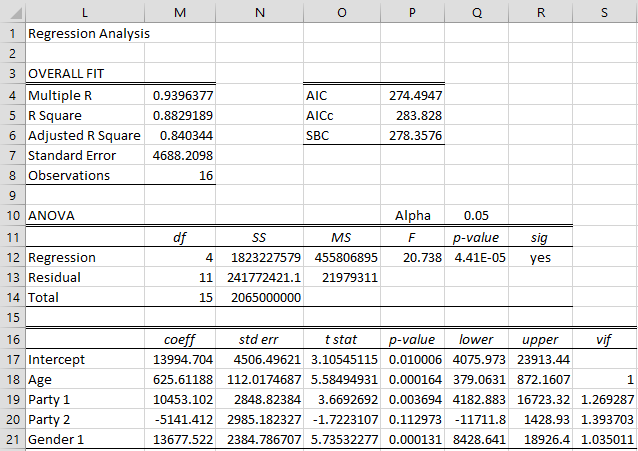
Categorical Coding Regression Real Statistics Using Excel
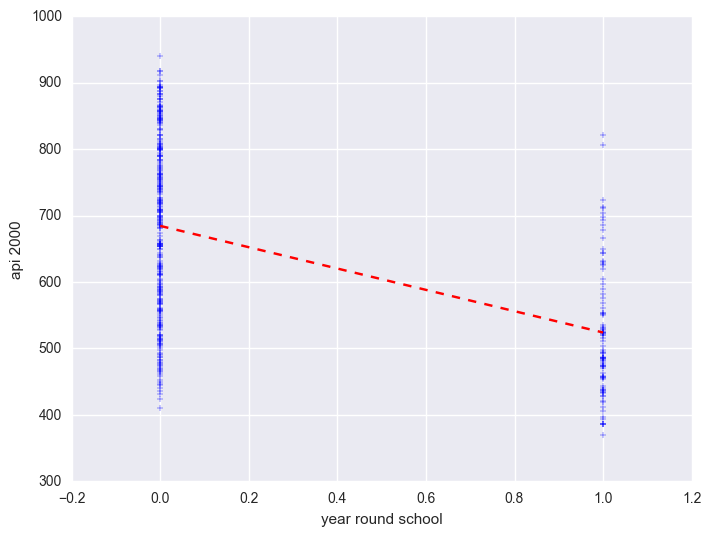
Linear Regression In Python Chapter 3 Regression With Categorical Predictors Pydata

Pin On How To Conduct Research And Statistics

Introduction To R For Data Science Session 6 Linear Regression Model In R Eda And Normality Tests R Blogge Data Science Linear Regression Regression
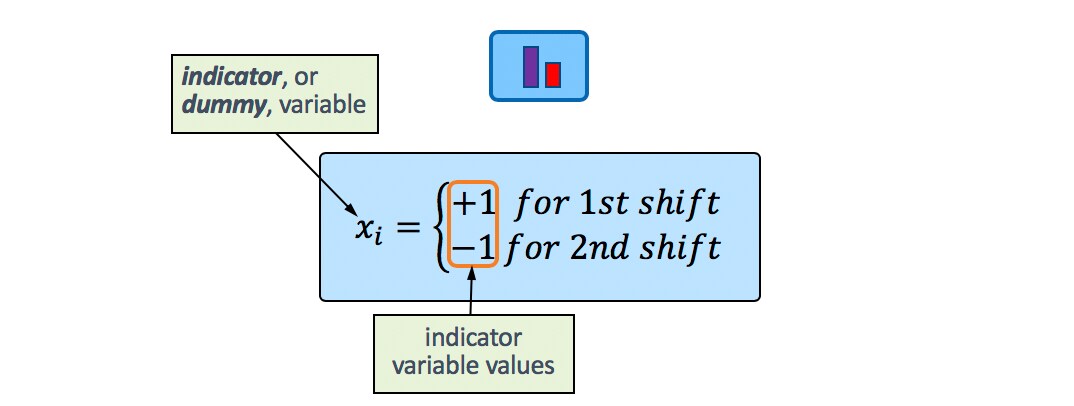
Multiple Regression With Categorical Predictors Introduction To Statistics Jmp

Plotting Lm And Glm Models With Ggplot Rstats Logistic Regression Linear Regression Confidence Interval
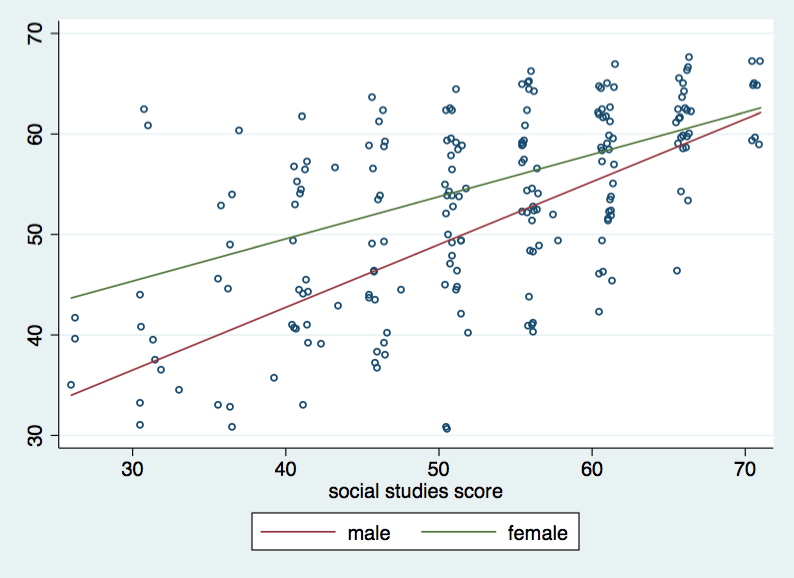
How Can I Understand A Categorical By Continuous Interaction Stata 12 Stata Faq

A Simple Linear Regression Model Statistics Math Data Science Research Skills
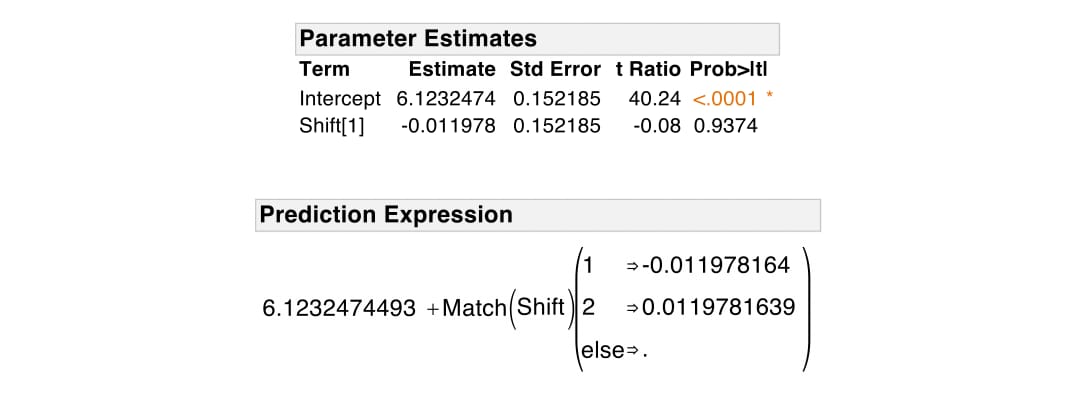
Multiple Regression With Categorical Predictors Introduction To Statistics Jmp

Posting Komentar